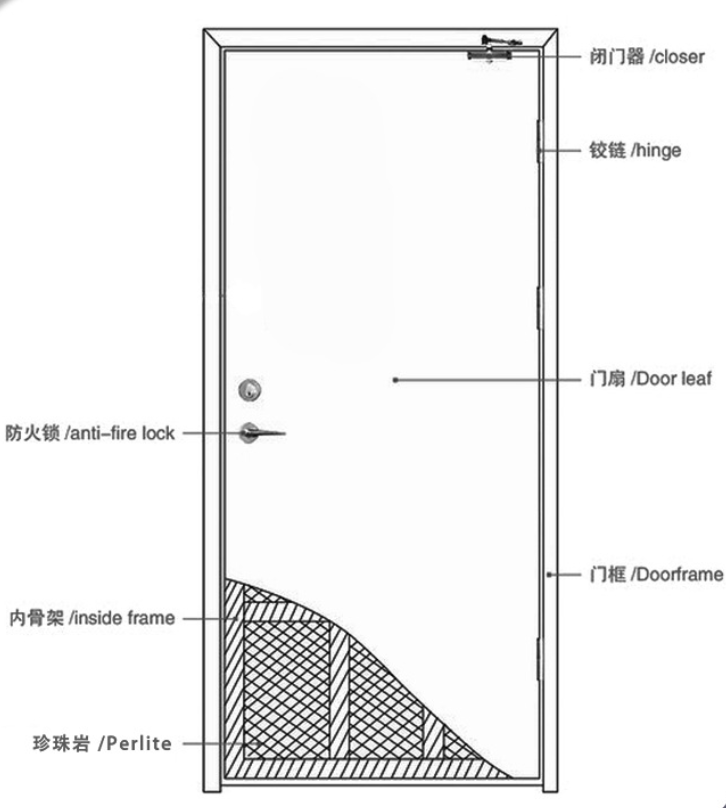
Key Differences Between UL-Certified and European Standard-Certified Fire Doors
1. Differences in Certification Standards and Testing Methods
UL certification follows U.S. standards (UL 10B/UL 10C), using a "time-temperature curve" test where furnace temperatures reach 538°C in 5 minutes and 927°C in 30 minutes, simulating flash-fire conditions. Certified doors are labeled with fire resistance durations (e.g., 20/45/60/90 minutes).
European certification complies with EN 1634-1, featuring a slower temperature rise (821°C in 30 minutes) but additional evaluations for insulation (unexposed surface ≤180°C) and radiation (≤15 kW/m² at 1m distance). For example, an EI60-rated door must withstand 60 minutes of fire while maintaining insulation.
Key Differences:
UL prioritizes structural integrity under extreme heat; European standards demand better insulation.
European certification requires 200,000 open-close cycle tests (EN 1191); UL has no mandatory durability test.
2. Material and Structural Parameters Compared
Typical UL-Certified Door Construction:
Core: Ceramic fiber or mineral wool (density ≥110kg/m³), strong fire resistance but weaker insulation.
Metal Edging: Steel frame ≥1.2mm thick, door leaf ≥0.8mm.
Seals: Intumescent graphite strips expanding 5–10x to block smoke.
European-Certified Door Design:
Core: Vermiculite boards or composite panels (density ≥150kg/m³), balancing fire resistance and insulation.
Hardware: Hinges and closers must meet EN 1634-3, with ≥80kg load capacity.
Gap Control: ≤3mm gaps, paired with dual-component seals (e.g., silicone + graphite).
Performance Comparison (60-Minute Rating Example):
| Parameter | UL-Certified Door | European EI60 Door |
|---|---|---|
| Max Unexposed Temp. | Not regulated | ≤180°C |
| Radiation Limit | Not tested | ≤15 kW/m² |
| Allowable Door Warping | ≤6mm | ≤3mm |
3. Applications and Regulatory Compliance
UL-Certified Doors Are Ideal For:
Mandatory in North America (e.g., NFPA 80 compliance).
High-risk environments like petrochemical plants/data centers (superior fire resistance).
European-Certified Doors Excel In:
EU, Middle East, and Southeast Asian projects (CPR Regulation compliance).
Public buildings (hospitals, schools) requiring strict insulation and smoke control.
Case Study:A Dubai hotel project needing both UL (for U.S. contractors) and European (local fire codes) certifications opted for dual-certified doors, increasing costs by 15–20% but avoiding retrofit expenses.
4. Selection Guide: Matching Certification to Needs
Regulations First: UL for the U.S., European for the EU; China’s GB standards partially align with European norms.
Performance Priorities: Choose European EI ratings for insulation/smoke control; UL for pure fire resistance.
Cost Considerations: European-certified doors cost 10–15% more due to additional testing.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can UL and European certifications be used interchangeably?No. Regulations are region-specific—European authorities don’t accept UL as a CE mark substitute, and vice versa.
Q2: How do fire resistance ratings compare between standards?UL 60 minutes ≈ European EI30 (UL’s steeper test curve makes it more stringent).
Q3: Why does European certification impose stricter hardware requirements?European standards ensure doors remain operational during fires, mandating durable hinges/closers.
Q4: Are dual-certified doors superior?Yes, but costlier. Ideal for global projects (e.g., Middle East often requires UL + European certifications).
Q5: Does installation affect certification validity?Yes! Non-certified installers or substandard hardware (e.g., non-fire-rated locks) may void certification.
Recommended Products
up to dateSeychelles Automatic Door Accessories
- Manufacturers Foot Pedal Activator Safety Beam Photocell Barrier Sensor For Medical Sliding Doors
- Safety photoelectric switch for high-speed door sensors
- Durable PVC Fast Rolling Door Fittings for Enhanced Security
- Automatic Repair of Zipper Door Plastic/Polymer Rails
- Smart Automatic Door Sensor for Fast Rolling Access Control
- Soft Fast Gate Control System 1.5kw Servo Motor and Control Box
- Automatic Access Control Square Surface Mount Infrared Non-Contact Switch
- Explosion-Proof Reinforced Self-Limiting Electric Heating Belt
- Explosion-Proof Shielded Self-Controlling Temperature Electric Heating Belt
- Heating Belt for Anti-Freezing, Heating and Heat Preservation of Cold Storage Doors
- 40W flame retardant explosion-proof self-limiting electric heating belt
- High Speed Door Zippers Industrial Door Zippers
- Safety Beam Sensor Use for Automatic Door
- Wireless Hand Sensor Switch For Automatic Door
- Hospital Door Foot Sensor
- Automatic Sliding Door System Wireless Touch Press Switch
- Automatic Sliding Door IP65 Waterprooft Wireless Hand Press Switch
- Automatic Door Microwave Sensor
- Reflective Type Infrared Detector
- Automatic High Speed Door Infrared Radar Sensor CNB-204G